Human torso model labeled organs provide an invaluable tool for understanding the intricate workings of the human body. These models offer a comprehensive representation of the organs, their location, and their interrelationships, making them essential for medical education, patient care, and scientific research.
This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of human torso model labeled organs, exploring their applications, design considerations, and advanced features. By providing a detailed overview of the organs and their functions, this guide empowers readers with a deeper understanding of human anatomy and physiology.
1. Human Torso Model Overview
Human torso models labeled with organs are essential tools for teaching and understanding human anatomy. They provide a detailed and accurate representation of the internal organs, allowing students and healthcare professionals to visualize and study the complex structures of the human body.
These models come in various materials, including plastic, resin, and latex, each offering different levels of durability and detail. Some models may include removable organs or cross-sectional views, enabling a deeper exploration of the body’s internal structures.
Labeled human torso models are widely used in medical and nursing education, providing students with a hands-on and interactive way to learn about human anatomy and physiology. They also serve as valuable tools in medical practice, assisting healthcare professionals in diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient education.
2. Organ Labeling and Anatomy
Labeled human torso models typically depict a wide range of organs, including:
- Heart
- Lungs
- Liver
- Stomach
- Intestines
- Kidneys
- Pancreas
- Uterus
- Ovaries
- Testes
Each organ is labeled with its name and anatomical location, providing a clear understanding of its position within the body. The models also show the relationships between different organs and their respective systems, such as the circulatory, respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems.
3. Applications in Education
Labeled human torso models are widely used in medical and nursing education to enhance the teaching and learning of human anatomy and physiology. They offer several benefits:
- Visual Representation:Models provide a tangible and realistic representation of the human body, allowing students to visualize complex anatomical structures in three dimensions.
- Interactive Learning:Models enable hands-on exploration, allowing students to examine organs, manipulate them, and understand their spatial relationships.
- Enhanced Understanding:By studying labeled models, students gain a deeper understanding of the location, function, and interconnections of different organs.
- Improved Retention:Visual and interactive learning through models helps improve memory and retention of anatomical information.
4. Applications in Medical Practice
Labeled human torso models are also valuable tools in medical practice, providing assistance in diagnosis and treatment planning:
- Patient Education:Models help healthcare professionals explain complex medical concepts to patients in a clear and visual manner.
- Treatment Planning:Models provide a three-dimensional representation of the patient’s anatomy, allowing healthcare professionals to plan surgical procedures or other interventions.
- Diagnosis:Models can assist in identifying anatomical abnormalities or pathological conditions, aiding in the diagnostic process.
- Improved Communication:Models facilitate communication between healthcare professionals, patients, and families, fostering a shared understanding of the patient’s condition.
5. Design Considerations
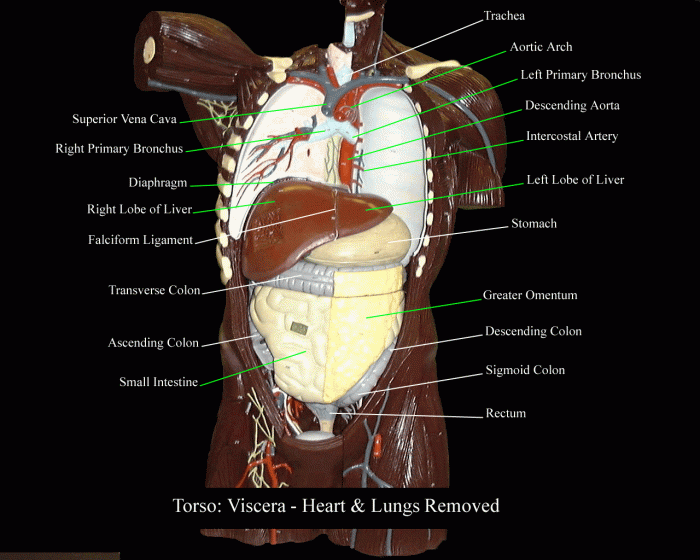
Creating an effective human torso model labeled with organs requires careful consideration of several design factors:
- Accuracy:Models should be anatomically accurate, ensuring that organs are represented in their correct location and proportion.
- Detail:Models should provide sufficient detail to allow for proper identification and understanding of organs and their structures.
- Durability:Models should be made of durable materials that can withstand repeated handling and use in educational and clinical settings.
- Visual Cues:Color-coding, shading, or other visual cues can enhance the model’s clarity and ease of use.
- Removable Organs:Some models feature removable organs, allowing for deeper exploration and understanding of internal structures.
6. Advanced Features
Some human torso models incorporate advanced features to enhance their educational and medical value:
- Cross-sectional Views:Models with cross-sectional views provide a detailed look at internal structures and their relationships.
- Interactive Digital Components:Models with interactive digital components allow users to access additional information, such as videos, animations, or quizzes.
- Removable Organs:Models with removable organs facilitate detailed examination and understanding of organ structures and functions.
- Transparent Windows:Transparent windows allow users to visualize internal structures without having to remove organs.
Question Bank: Human Torso Model Labeled Organs
What are the benefits of using human torso model labeled organs?
Human torso model labeled organs offer numerous benefits, including enhanced understanding of anatomy, improved teaching effectiveness, and more accurate medical diagnosis and treatment planning.
What are the different types of human torso models available?
Human torso models vary in materials, features, and level of detail. They can be made from materials such as plastic, resin, or silicone, and may include removable organs, cross-sectional views, and interactive digital components.
How are human torso model labeled organs used in medical education?
Human torso model labeled organs are widely used in medical education to teach anatomy and physiology. They provide students with a hands-on, interactive way to learn about the human body, enhancing their understanding and retention of complex concepts.
