Identify cabling standards and technologies – Embark on a comprehensive exploration of cabling standards and technologies, unlocking the secrets to a seamless and efficient network infrastructure. This in-depth guide will illuminate the purpose, benefits, and diverse types of cabling standards, empowering you to make informed decisions for your cabling needs.
Delve into the realm of cabling technologies, where you’ll discover the advantages and limitations of each type. From traditional copper cables to cutting-edge fiber optics, we’ll unveil the ideal applications for each technology, ensuring optimal performance for your network.
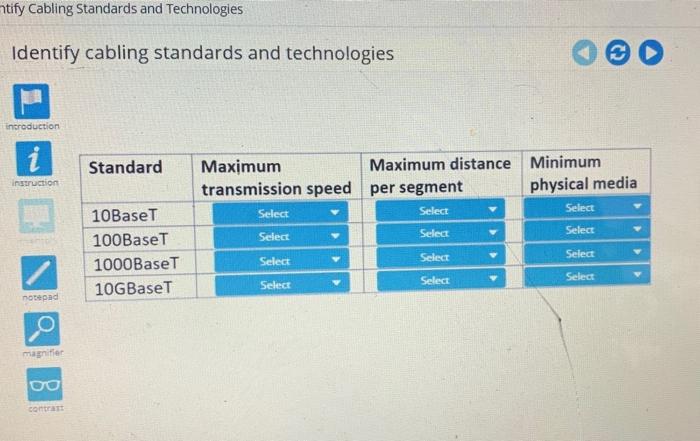
Cabling Standards
Cabling standards are a set of rules and guidelines that define the physical and electrical characteristics of cables and connectors used in telecommunications networks. They ensure that cables and connectors are compatible with each other and meet the performance requirements of the network.
Adhering to cabling standards has several benefits, including:
- Improved network performance and reliability
- Reduced installation time and costs
- Enhanced safety and compliance with regulations
Some common cabling standards include:
- TIA/EIA-568-A and TIA/EIA-568-B (for copper twisted pair cabling)
- ISO/IEC 11801 (for fiber optic cabling)
- IEEE 802.3 (for Ethernet cabling)
When selecting a cabling standard, factors to consider include:
- Network requirements (e.g., bandwidth, distance, and latency)
- Cost
- Ease of installation
- Compatibility with existing infrastructure
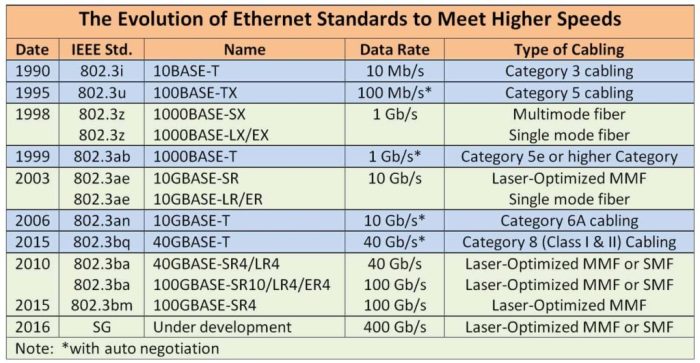
Cabling Technologies
Cabling technologies refer to the different types of cables used in telecommunications networks. Each technology has its own advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for specific applications.
Copper Twisted Pair (UTP), Identify cabling standards and technologies
UTP cables consist of four pairs of copper wires twisted together. They are commonly used in Ethernet networks and telephone systems.
Advantages:
- Low cost
- Easy to install
- Widely available
Disadvantages:
- Limited bandwidth and distance
- Susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI)
Fiber Optic
Fiber optic cables transmit data using light signals through glass or plastic fibers. They offer high bandwidth and long distances.
Advantages:
- Very high bandwidth
- Low loss and long distances
- Immune to EMI
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than copper cables
- More difficult to install
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cables consist of a central copper conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulator and a braided shield. They are used in cable television and broadband internet.
Advantages:
- Higher bandwidth than UTP cables
- Less susceptible to EMI than UTP cables
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than UTP cables
- Bulkier and less flexible than UTP cables
Emerging Trends in Cabling Technologies
Some emerging trends in cabling technologies include:
- The use of Category 8 (Cat 8) cables for high-speed Ethernet networks
- The development of multi-pair copper cables for increased bandwidth
- The adoption of fiber optic cables for long-distance and high-bandwidth applications
Cabling Design
Cabling design involves the planning and layout of a cabling system to meet the specific requirements of a network.
The steps involved in cabling design include:
- Network assessment: Determining the network’s requirements and constraints
- Topology selection: Choosing the appropriate cabling topology (e.g., star, bus, or ring)
- Cable selection: Selecting the appropriate cable type and category based on network requirements
- Route planning: Determining the path of the cables and avoiding potential obstacles
- Documentation: Creating a detailed plan of the cabling system for future reference
Proper cabling design is important for:
- Ensuring optimal network performance
- Reducing cable clutter and improving aesthetics
- Facilitating future network upgrades and expansions
Best practices for cabling design include:
- Using structured cabling systems for ease of management and scalability
- Following industry standards and guidelines to ensure compatibility and reliability
- Labeling and documenting all cables and connections for easy identification
- Using cable management systems to organize and protect cables
Software tools can be used to assist with cabling design. These tools provide features such as automated cable routing, collision detection, and documentation generation.
FAQs: Identify Cabling Standards And Technologies
What is the primary purpose of cabling standards?
Cabling standards provide a set of guidelines and specifications that ensure the compatibility, safety, and performance of cabling systems, enabling seamless communication and data transmission.
Why is it important to adhere to cabling standards?
Adhering to cabling standards minimizes signal interference, ensures proper data transmission rates, enhances network security, and facilitates troubleshooting and maintenance.
What are some common examples of cabling standards?
Common cabling standards include ANSI/TIA-568, ISO/IEC 11801, and EN 50173, which provide guidelines for structured cabling systems, fiber optic cables, and data center cabling, respectively.
What factors should be considered when selecting a cabling standard?
Factors to consider include the application, network requirements, budget, environmental conditions, and future expansion plans.